Imec simulation framework predicts thermal transport in RF devices for 5G and 6G
This week, at the 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting (IEEE IEDM 2022), imec, a global research and innovation hub in nanoelectronics and digital technologies, presents a Monte Carlo Boltzmann modelling framework that uses microscopic heat carrier distributions to predict 3D thermal transport in advanced RF devices intended for 5G and 6G wireless communication for the first time.
Case studies with GaN high-electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs) and InP heterojunction bipolar transistors (HBTs) revealed peak temperature rises that are up to three times larger than conventional predictions with bulk material properties. Imec’s new tool will be useful in guiding optimisations of next-gen RF devices toward thermally improved designs.
GaN- and InP-based devices have emerged as interesting candidates for 5Gmm-wave and 6G sub-THz mobile front-end applications, respectively, due to their high output power and efficiency. To optimise these devices for RF applications and make them cost-effective, much attention is paid to upscaling the III/V technologies to a Si platform and making them CMOS compatible. However, with shrinking feature sizes and rising power levels, self-heating has become a major reliability concern, potentially limiting further RF device scaling.
Nadine Collaert, Programme Director of Advanced RF at imec: “Tuning the design of GaN- and InP-based devices for optimal electrical performance often worsens thermal performance at high operating frequencies. For GaN-on-Si devices, for example, we recently achieved tremendous progress in electrical performance, bringing the power-added efficiencies and output power for the first time on par with that of GaN-on-silicon carbide (SiC). But further enlarging device operating frequency will require downsizing the existing architectures. In these confined multilayer structures, however, thermal transport is no longer diffusive, challenging accurate self-heating predictions. Our novel simulation framework, yielding good matches with our GaN-on-Si thermal measurements, revealed peak temperature rises up to three times larger than previously predicted. It will provide guidance in optimising these RF device layouts early in the development phase to ensure the right trade-off between electrical and thermal performance.”
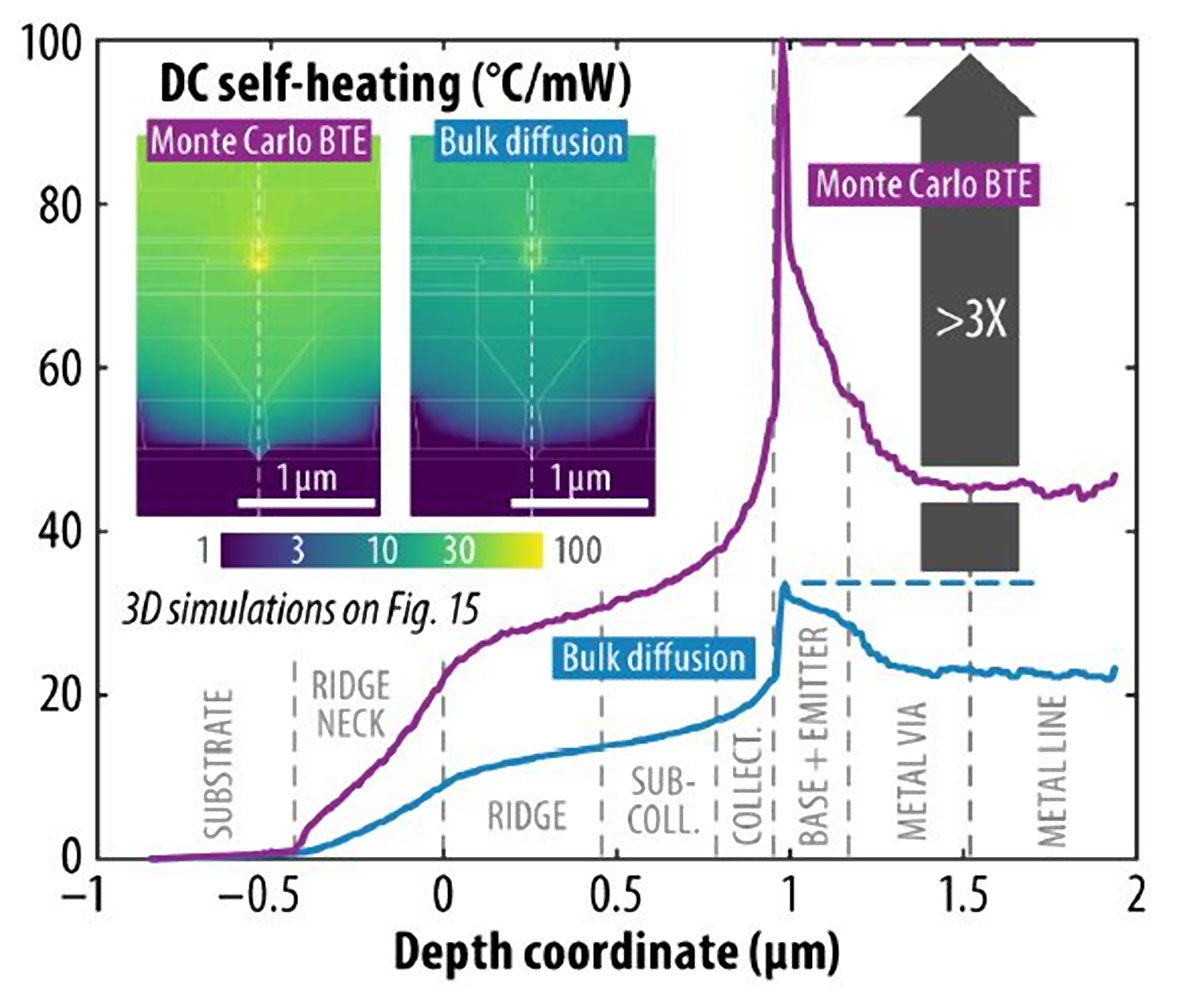
Such guidance also proves very valuable for the novel InP HBTs, where imec’s modelling framework highlights the substantial impact non-diffusive transport has on self-heating in complex scaled architectures. For these devices, nanoridge engineering (NRE) is an interesting heterogeneous integration approach from an electrical performance point of view.
“While the tapered ridge bottoms enable low defect density within the III-V materials, they, however, induce a thermal bottleneck for heat removal towards the substrate,” explains Bjorn Vermeersch, Principal Member of Technical Staff in the Thermal Modelling and Characterisation Team at imec. “Our 3D Monte Carlo simulations of NRE InP HBTs indicate that the ridge topology raises the thermal resistance by over 20 percent compared to a hypothetical monolithic mesa of the same height. Our analyses furthermore highlight the direct impact of the ridge material (e.g., InP vs. InGaAs) on self-heating, providing an additional knob to improve the designs thermally.”
These results are presented in two invited papers at the 2022 IEDM, by Bjorn Vermeersch, on thermal modelling, and by Nadine Collaert, on GaN and InP technologies for next-generation high-capacity wireless communication, respectively [papers 11.5 and 15.3].
Figure 1 - Measured and predicted thermal resistance vs. finger width of two-finger GaN-on-Si HEMTs
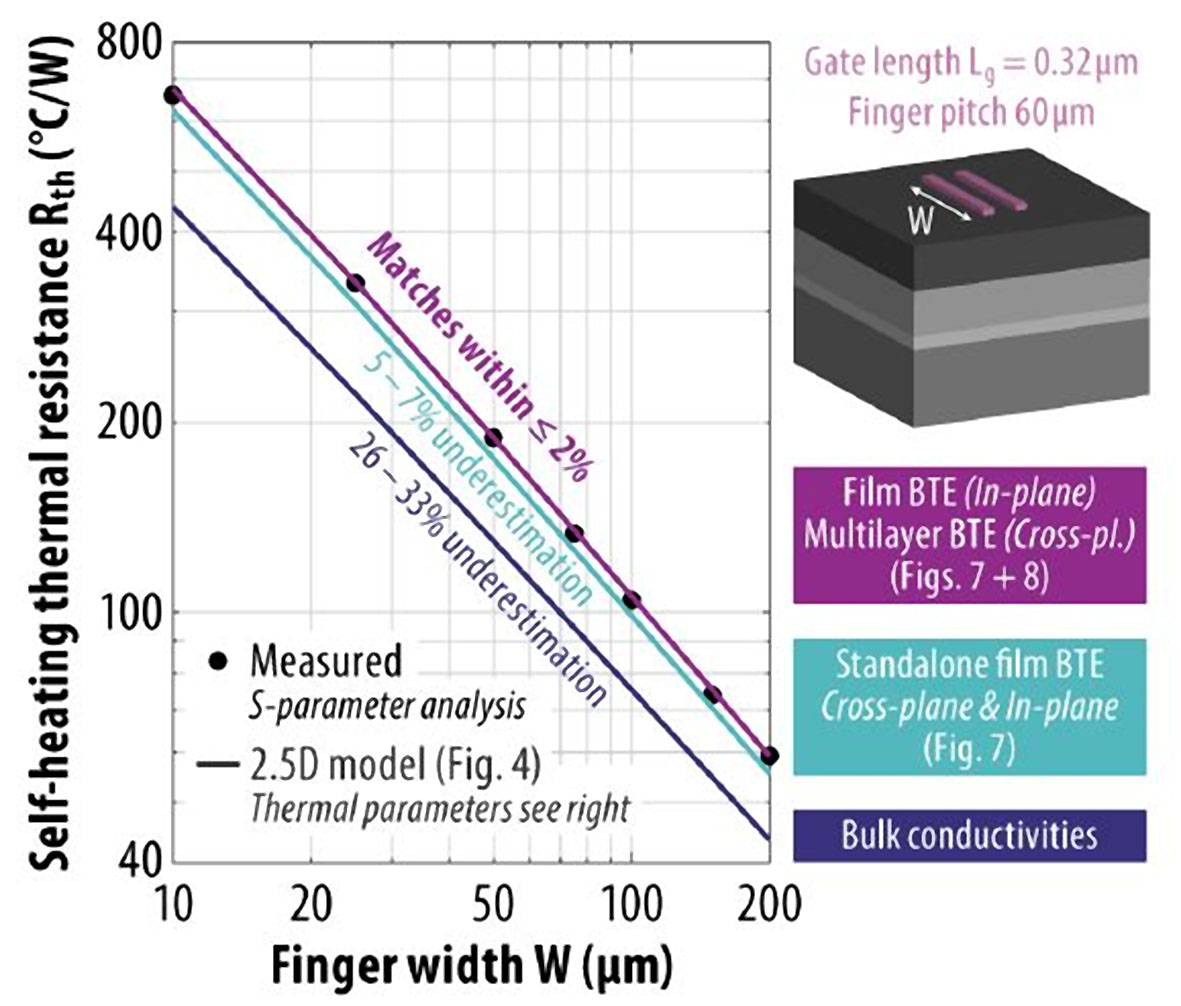
Figure 2 – Geometry of the InP nanoridge HBT used in the 3D simulation
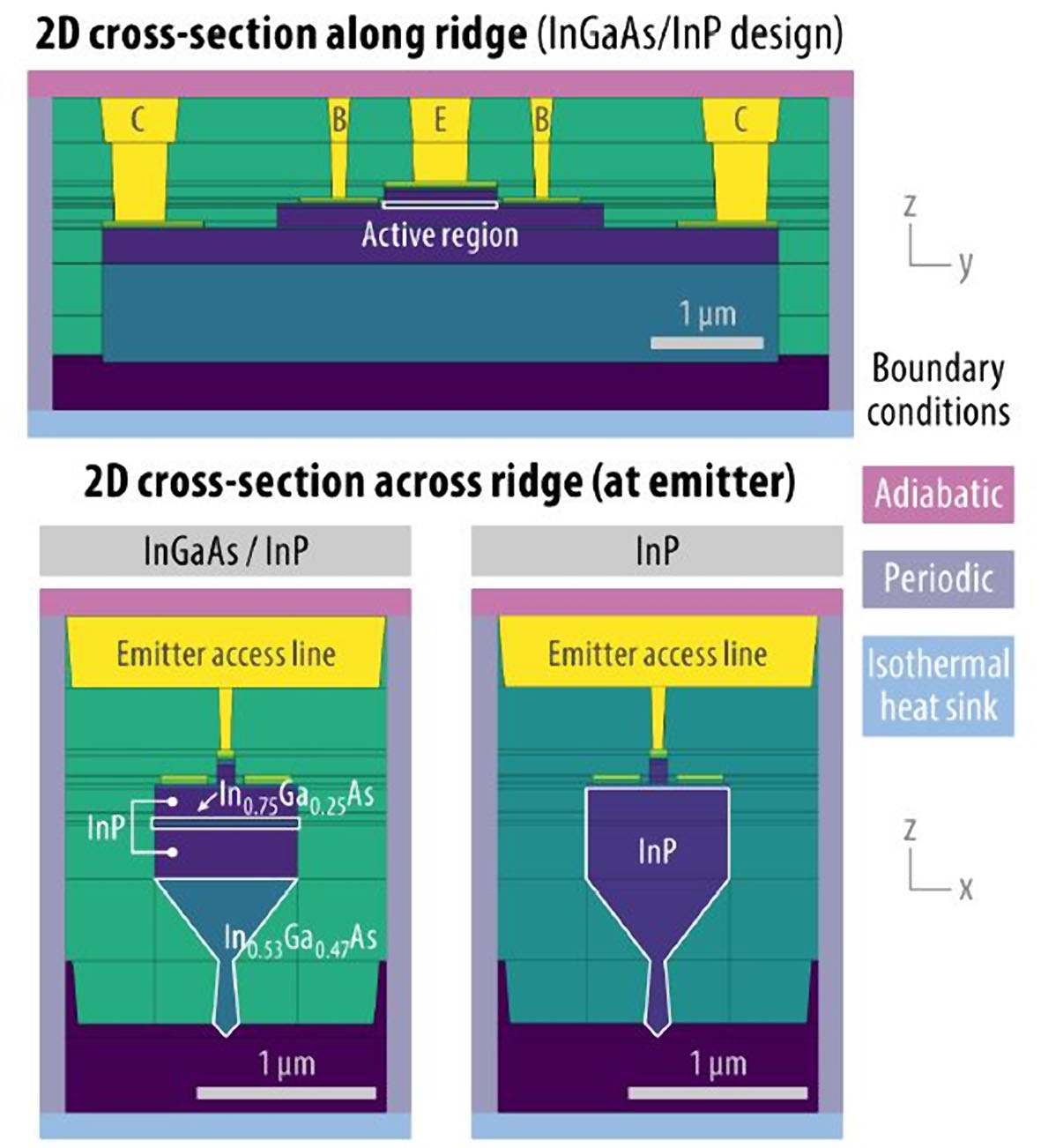
Figure 3 – Impact of non-diffusive thermal transport effects (as captured by imec’s Monte Carlo simulation) in InP nanoridge HBTs