Connecting electric vehicles to the power grid
Engineers at Fraunhofer ESK have specified and implemented the required communication interface as part of the EU-sponsored smart vehicle-to-grid interface (SMARTV2G) project. This project aims to create a system in which electric vehicles use and temporarily store energy. By temporarily storing the energy, it can be fed back into the grid as needed.
As part of the SmartV2G project, engineers analyzed all of the information flows needed to support vehicle-to-grid integration. With this basis, they set about identifying the relevant infrastructure components, designing the underlying communication architecture, and deriving the functional and technical specifications. Once this had been done, the engineers implemented and evaluated the communication path. Providing a more convenient driving experience leading to improved energy efficiency and lower costs, extensive communication occurs between the energy management system and the electric vehicle: information such as location, opening hours, number of open charging stations, current energy rates and available payment options.
This vast exchange of information can benefit the driver in several ways, e.g. a charging station within the vehicle’s estimated operating range can be reserved even while driving. Automatic vehicle identification also offers advantages to drivers, by considering individual preferences such as planned driving routes and simplified billing models. Optimally utilising the capacity of the grid, time-shifted charging could contribute to maintaining a stable energy network. Since sufficient renewable energy supplies are not always on-hand, this is a key issue for energy providers and operators who require highly flexible drivers. The SmartV2G project innovations will ultimately benefit consumers, energy providers and grid operators alike.
Researchers are driving the development of a uniform manufacture-independent specification for the E-vehicle-to-charging station communication through ISO/IEC15118. This standard will define a comprehensive exchange of information that is essential for the “smart” charging process. Communication between the charging station and the smart grid will be based on an enhancement of the IEC 61850 global standard. By combining the two standards, the charging station is transformed into a node that integrates the electric vehicle charging process into the smart grid. This gives drivers access to variable energy rates and also allows the energy provider or grid operator to integrate the electric vehicle into the energy management system of the smart grid.
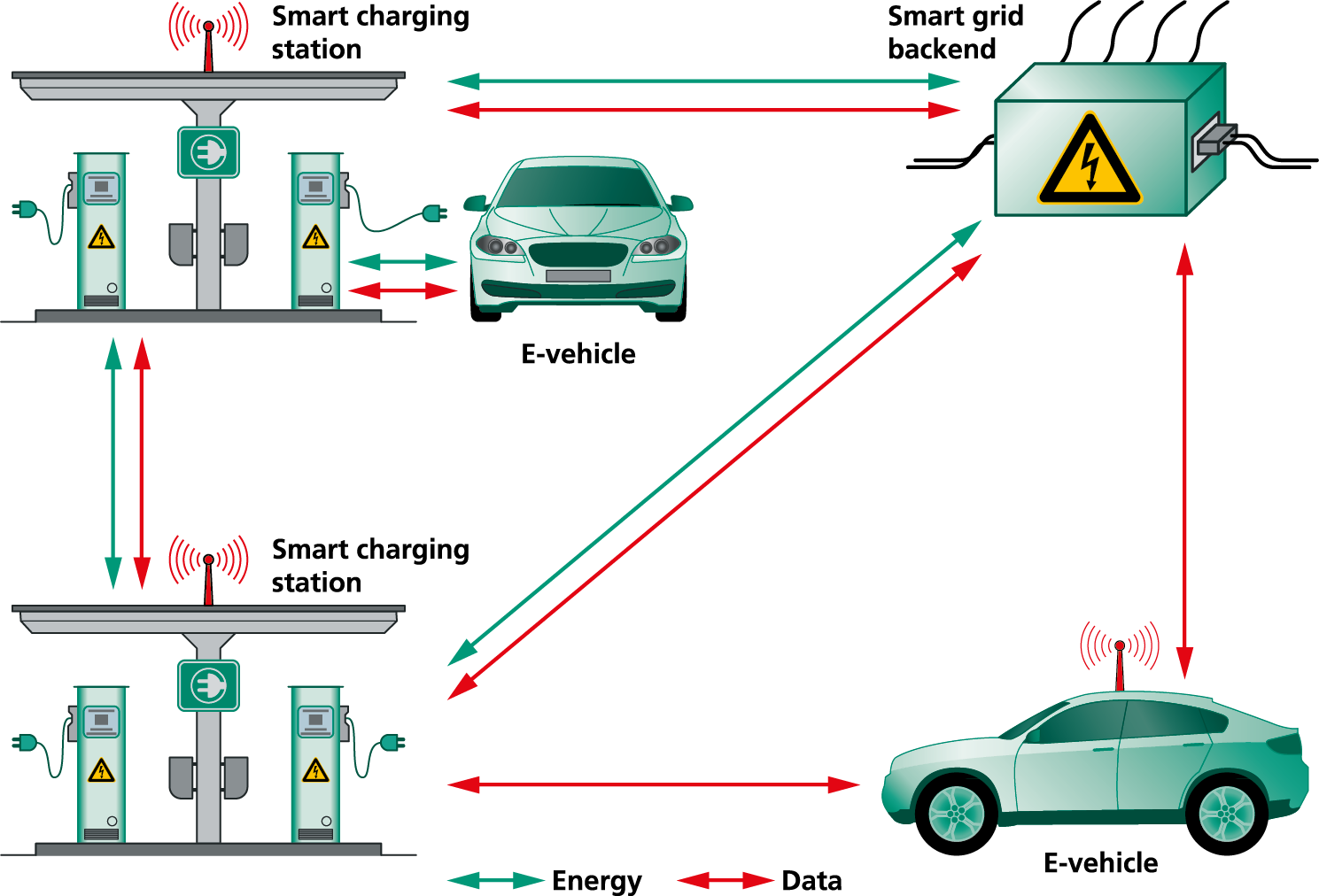
A demonstrator developed by Fraunhofer ESK runs through the entire information chain, from the vehicle to the control center energy management system. This results in the exchange of a variety of information such as battery status, charging progress, charging mode, authentication data and price and payment information.
The SMARTV2G project is being funded through the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program.





