Technology can anonymise encrypted personal data
Hitachi announced the development of technology to securely anonymise encrypted personal data. Anonymisation converts information related to individuals, personal information, to a form which cannot identify the individual. This newly developed technology which conducts anonymisation in a more secure manner will be applied to respond to the expected increase in market needs for anonymised personal data resulting from the revision of the Japanese legislation on the Protection of Personal Information in September 2015.
In recent years, the amount and variety of data generated and collected has continued to grow with the increased use of mobile phones and sensor equipment, and big data analytics is being applied in many fields to derive value from this data.
With the implementation of the revised Protection of Personal Information Act, not only will data collected from equipment but also anonymised information, that is personal data which has been processed in a way to prevent distinguishing individuals, will be legally available for third party use in the future. As a result, it can be expected that the usage of anonymised personal data will increase significantly, such as in high accuracy market research on people's movement and purchasing transactions.
The use of cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular in such big data analytics, as it allows flexibility in computing processing power. In handling sensitive data such as personal information, however, even greater security is required. Technology is being developed for practical application that encrypts data on the cloud in a form which cannot be easily decrypted by third parties but allows search and analytics to be conducted.
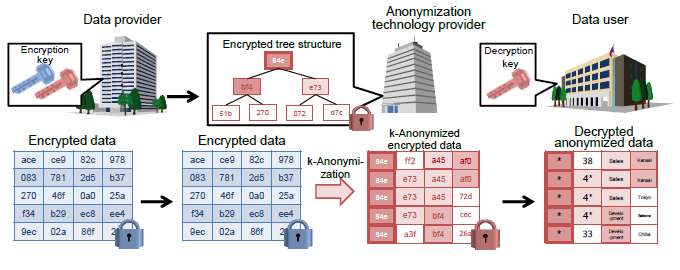
On the other hand, k-anonymisation technology is a well-known technology for anonymising personal data but with conventional technology, pre-encrypted data cannot be directly anonymised and had to be decrypted first for anonymisation, thus raising security issues.
To enhance security in the anonymisation of personal data, Hitachi has developed technology to encrypt personal data and enable k-anonymisation of the encrypted data on the cloud. Features of the technology developed are as follows:
1. Secure generalisation of encrypted data
Many k-anonymisation technologies use a tree structure to generalise similar data of different values, grouping data from a smaller group into a larger group in a hierarchy to anonymise the data. For example, data from the smaller regional subsets, Kanto (10 items) and Tohoku (20 items), can be anonymised by generalising the data (30 items) in a bigger regional subset, East Japan. With conventional technology however, this tree structure could not be formed from encrypted data as the information on the smaller subset could not be read.
Hitachi applied its original technology that can compare encrypted data to determine whether given subset values are the same, to develop technology which sums up the number of subsets with the same value, and uses the aggregated data to create a tree structure. This tree structure also minimises information loss through generalisation by assigning the encrypted data in the smaller groups with less similar values to a lower position and the larger groups with more similar values to a higher position in the hierarchy.
2. High speed processing and high data security
In general, processing encrypted data is significantly slower than processing non-encrypted data. Using Hitachi's searchable encryption technology, comparison between encrypted data can be performed at high-speed as well as minimising the amount of data processing required in the encrypted state. As a result, the overhead increase in data processing can kept within 30% to successfully ensure practical processing speeds.
Further, to ensure even higher security, different encryption keys are used to encrypt the data and anonymise the encrypted data. As a result, security can be guaranteed should the encrypted data accidently leak before anonymisation as only the data provider holds the decryption key.
Hitachi aims to use this technology for commercialisation in FY2018 to cater to the increased use of personal data.
This technology achievement will be presented at the Technical Committee on Information Security to be held at the University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo, Japan, on 10th to 11th March 2016.










