Wireless power for ePaper displays
Engineers from E Ink and Powercast have collaborated to integrate RF wireless power technology into ePaper devices for low power, wireless charging to liberate screens and ease users’ range anxiety or fear of power loss
Pairing a wireless power solution with an ePaper screen can reduce the need to recharge batteries and even eliminate the need for batteries in some devices.
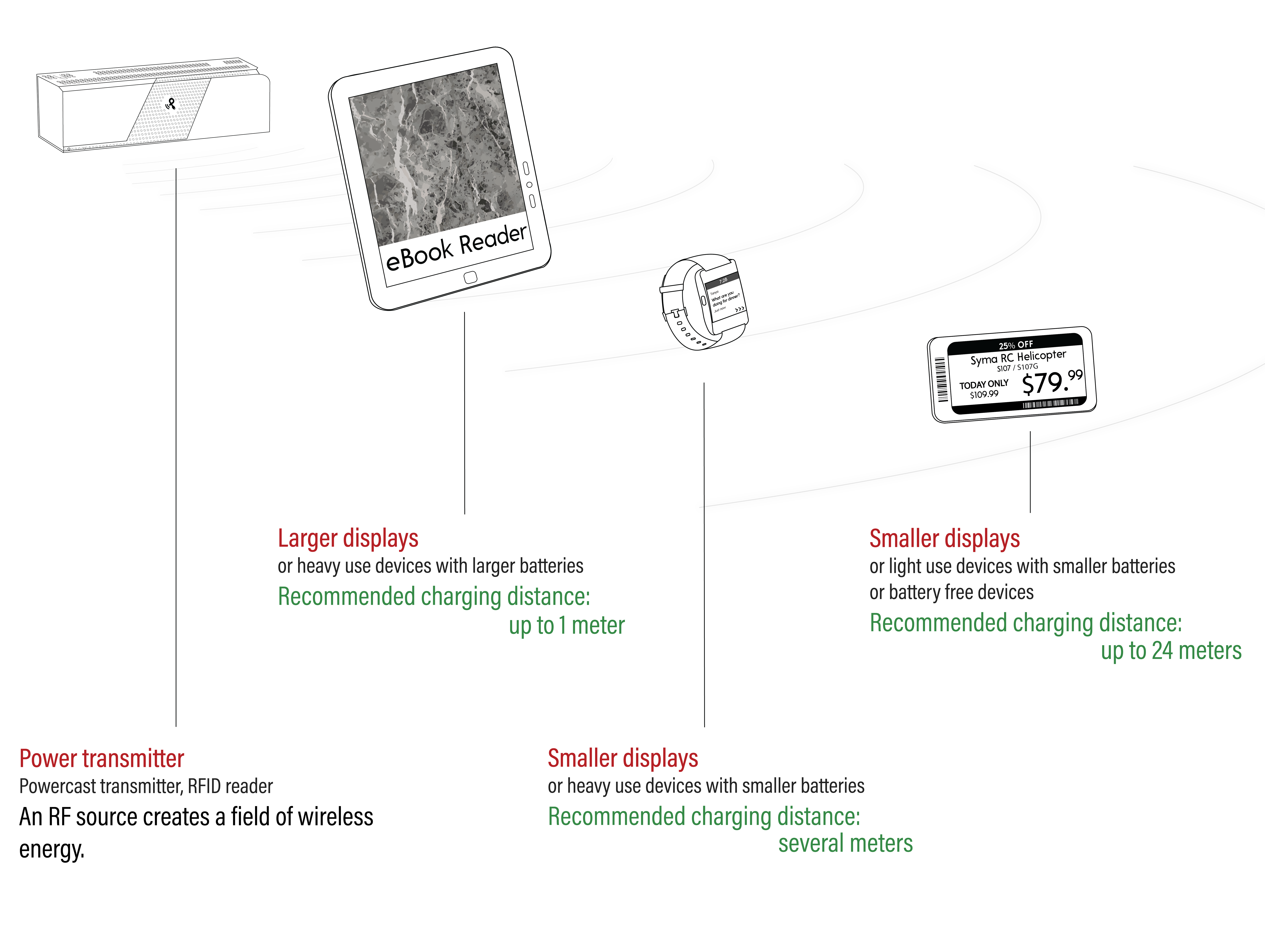
A wireless power system requires an RF power transmit source and Powercast’s Powerharvester RF-to-DC PCC110 converter chips with an antenna. A Powercast power transmitter or the existing RAIN RFID infrastructure can be used for a power source. One or more end devices fitted with Powerharvester receiver chips can harvest wireless energy for a range of functions, such as recharging eReaders, updating pricing information on electronic shelf edge labels and writing content for eBadges.
Distance and screen size
As a rule, more power is available at closer distances to a power source than there is available at farther distances. For this reason, it is recommended that more power-
hungry devices, such as e-readers or smart watches be recharged at close distance to a power transmitter. Devices which are less power-hungry or which require a screen update less frequently can operate effectively at further distances from their power source, up to 24m or 80ft (See Figure 1).
E Ink’s bi-stable ePaper screens operate at low power levels and require no additional power to maintain a written screen. The amount of power consumed can vary based on screen size and a variety of other factors, but as such a miniscule amount of energy is needed for the rewrite process, devices utilising E Ink screens can operate on very small batteries for extended periods of time.
Powercast’s RF wireless power technology is inherently a low-power system which can send wireless power over significant distances, up to 24m. These systems operate in the US and Canada at a 1W power output and the amount of power which is available to E Ink enabled devices increases as devices move closer to a power transmit unit. Even at long distances, Powercast says its technology trickle recharges batteries to extend the life of a battery. Screens which require infrequent updates, such as electronic shelf edge labels, can even become battery-free.
Travelling light
ViewTag (adopted as TAG by British Airways in 2019) uses a 4.05-inch E ink Mobius bi-state display to display airline traveller information. It replaces the traditional paper luggage tag, reduces costs to airlines and is an an environmentally-friendly alternative to paper-based luggage tags.
.png)
E Ink’s bi-stable displays allow devices the option of entering into a sleep mode once the screen has been written because no additional power is required to maintain the screen. A classic sleep mode still requires a trickle discharge of energy from the battery while the device awaits the next screen update command. After a long period, embedded batteries will still fully discharge despite only being used for a few screen updates.
The RF harvesting technology allows ViewTag to enter a mode of complete dormancy to preserve the battery when not being used for a screen update. The tag remains dormant until it detects and harvests RF from nearby airport RFID equipment, at which time it will update the screen if the tag is not already displaying the passenger’s current itinerary. There is no trickle discharge and the tag can to be reused for over 3,000 flights on a single battery.
Display labels
Electronic shelf edge labels can leverage existing retail RFID infrastructure for rechargeable or battery-free ePaper displays. The labels can be easily integrated into the existing price tag form factor and reduce costs by eliminating the communications radio of the display. Point-of-purchase displays and interactive advertising displays are other examples that can be wirelessly recharged or be battery-free using wireless power technology.
Visitor badges, employee nametags or access control cards can be updated and also eliminate paper waste while maintaining security standards. Information can be displayed accurately without worrying about the battery life.
In consumer electronics, larger devices such as e-readers with ePaper screens are perfect candidates for wireless charging. Benefits include the fact that no specific alignment is required and the battery tops up when not in use. Smart watches using ePaper screens offer longer battery lives than those with LCD screens and integrating a wireless charging option can significantly lengthen the periods between wired charging or even eliminate it altogether.
Author: Maria Singer is marketing and sales manager, Powercast







