Fujitsu and KDDI Research large-capacity multiband wavelength multiplexing transmission
Fujitsu Limited and KDDI Research has announced that they have successfully developed a large-capacity multiband wavelength multiplexing transmission technology using installed optical fibres.
The two companies have developed a technology that enables transmission of wavelength bands other than the C band, which has not been used in medium- and long-distance commercial optical communications, using a batch wavelength conversion and multiband amplification technology. The optical fibre communications network introduced with this technology enables wavelength transmission at 5.2 times the wavelength multiplicity of current commercial optical transmission technology. This enables the use of installed optical fibre facilities to increase communication traffic in a cost-effective and labour-efficient manner. The technology makes it easier to expand the transmission capacity in urban areas and densely populated residential areas where installation can prove challenging and offers the potential to significantly reduce the time required to start the service and reduce costs.
The development was undertaken as part of the ”Research and Development Project of the Enhanced Infrastructures for Post-5G Information and Communication Systems” commissioned by Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO).
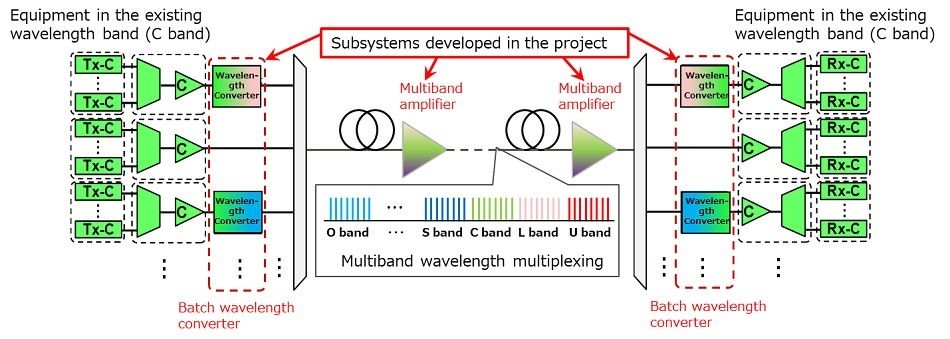
Figure 1: Image of the system applying high-capacity multiband wavelength multiplexing transmission technology
Project background
Amidst growing demand for services that leverage IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analysis, NEDO aims to strengthen the development and manufacturing base of Japan's post-5G information and communications systems by developing core technologies for post-5G information and communications systems. As part of this effort, from October 2020 to October 2023, Fujitsu and KDDI Research engaged in a project to enhance the performance of post-5G optical networks. Conventional commercial optical fibre communication networks use single-mode fibres in which light passes only through the centre of the optical fibre and use the C band (wavelength band: 1,530 nm to 1,565 nm) as the signal transmission band of the optical network. However, as the amount of communication traffic increases, the C band alone is expected to have insufficient transmission capacity. To increase the transmission capacity per fibre, the two companies aimed to increase the wavelength band used from the C band to the L band (1,565 nm to 1,625 nm), the S band (1,460 nm to 1,530 nm), the U band (1,625 nm to 1,675 nm), and the O band (1,260 nm to 1,360 nm), with the aim of making it multi-band.
Project results
As part of the project, Fujitsu built a simulation model that accounts for the degradation factors of transmission performance in multiband transmission, enabling the transmission design of multiband wavelength multiplexing systems. The simulation model reflects the measurement results of the commercial optical fibre characteristics and the transmission parameters extracted by the experimental system verification of the integrated wavelength converter/multiband amplifier. Using this model, Fujitsu realised high-precision simulations that reduce errors from the actual measurement to within 1dB, making it possible to take into account the interaction between bands and the degradation of transmission performance. KDDI Research’s research has made it possible to utilise twice the frequency bandwidth of the conventional C band in the O band, which has never been utilised in high-density wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) transmission. Combining both technologies, the two companies conducted actual transmission experiments using existing optical fibres and demonstrated multiband wavelength multiplexed transmission (transmission distance 45 km) in the O, S, C, L, and U bands (Figure 2), proving that wavelength transmission is possible at 5.2 times the wavelength multiplicity of conventional C-band-only transmission. The two companies also confirmed multi-band wavelength multiplexing transmission (transmission distance 560 km) in the S, C, L and U bands in the simulation.
Below is a description of the major research findings:
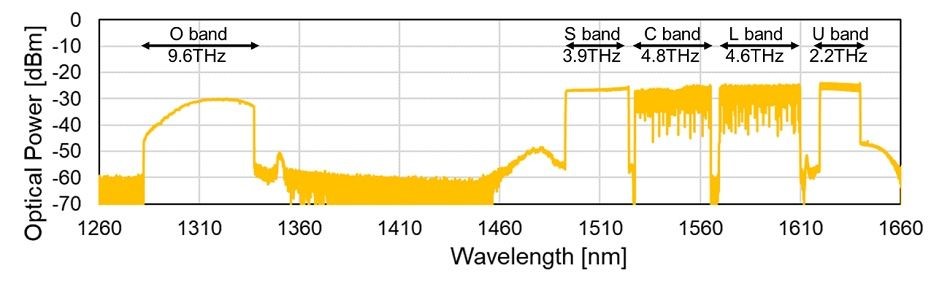
Figure 2: Received optical spectrum of a single installed fibre when the O, S, C, L, and U bands are transmitted simultaneously
Establishment of multiband dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) transmission technology
In the conventional design of a transmission system in the C band, parameters that could be treated as constants would not have practical problems, but in the case of multiband transmission over the S band + C band + L band + U band, the difference in transmission performance between the wavelength bands cannot be ignored, and a design that takes into account the wavelength dependence is required. For example, nonlinear degradation factors become more pronounced as the optical power input to the transmission line increases and as the transmission distance increases, thereby limiting transmission performance. In particular, stimulated Raman scattering (5), cross-phase modulation, and four-wave mixing caused by the interaction of light with multiple wavelengths are prominent at high wavelength multiplicities, which greatly affect the transmission performance of multiband wavelength multiplexing systems.
In this project, Fujitsu and KDDI Research established a design method for multi-band wavelength multiplexing systems by constructing a simulation model that takes into account the interaction between different bands and degradation factors in transmission performance. In addition, since wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical signals in the S and U bands are generated by all-optical signal processing technology from optical signals in the C and L bands, respectively, there is no need to use transmitters and receivers dedicated to the S and U bands. The integration of these technologies has enabled DWDM transmission in the S band + C band + L band + U band using coherent transmission technology, which leverages the phase of light, thus enabling high-speed and high-capacity communication.
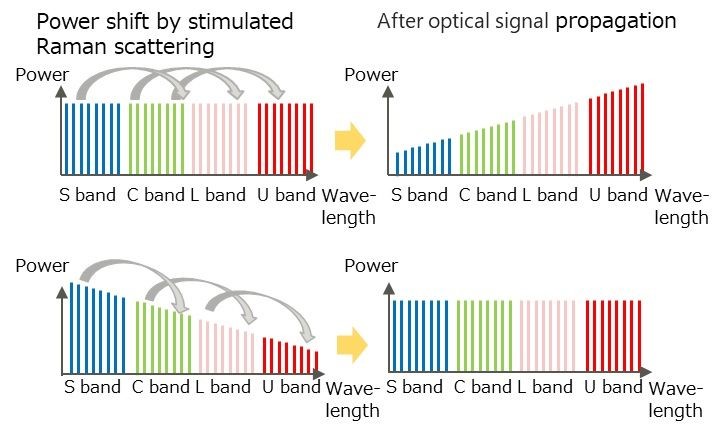
Figure 3: Transition of signal optical power between multibands by stimulated Raman scattering Above: The case without control, Below: The case with control so that the optical power distribution after fibre propagation is uniform
Establishment of coherent DWDM transmission technology in O band
Traditionally, coherent transmission technology has a tendency to distort O-band transmission signals due to the influence of other optical signal components. Moreover, non-linear noise, which often arises in the O-band, is generally difficult to eliminate with digital signal processing technology, thereby diminishing the overall system performance. As a result, applying coherent transmission technology in the O band has been challenging. Minimisation of nonlinear noise in the O band is possible by appropriately setting the transmitted optical power for each densely multiplexed wavelength signal. This approach minimised the effects of nonlinear noise and achieves coherent DWDM transmission over 9.6 THz in the O band, even if the process of signal compensation on the transmitter side and wavelength dispersion compensation on the receiver side was omitted. The O band, which is a wavelength band near zero dispersion, is less affected by wavelength dispersion and has the advantage of reducing the load on digital signal processing and improving energy efficiency.










