Towards 90% of cars connected in 2028: what are the driving forces?
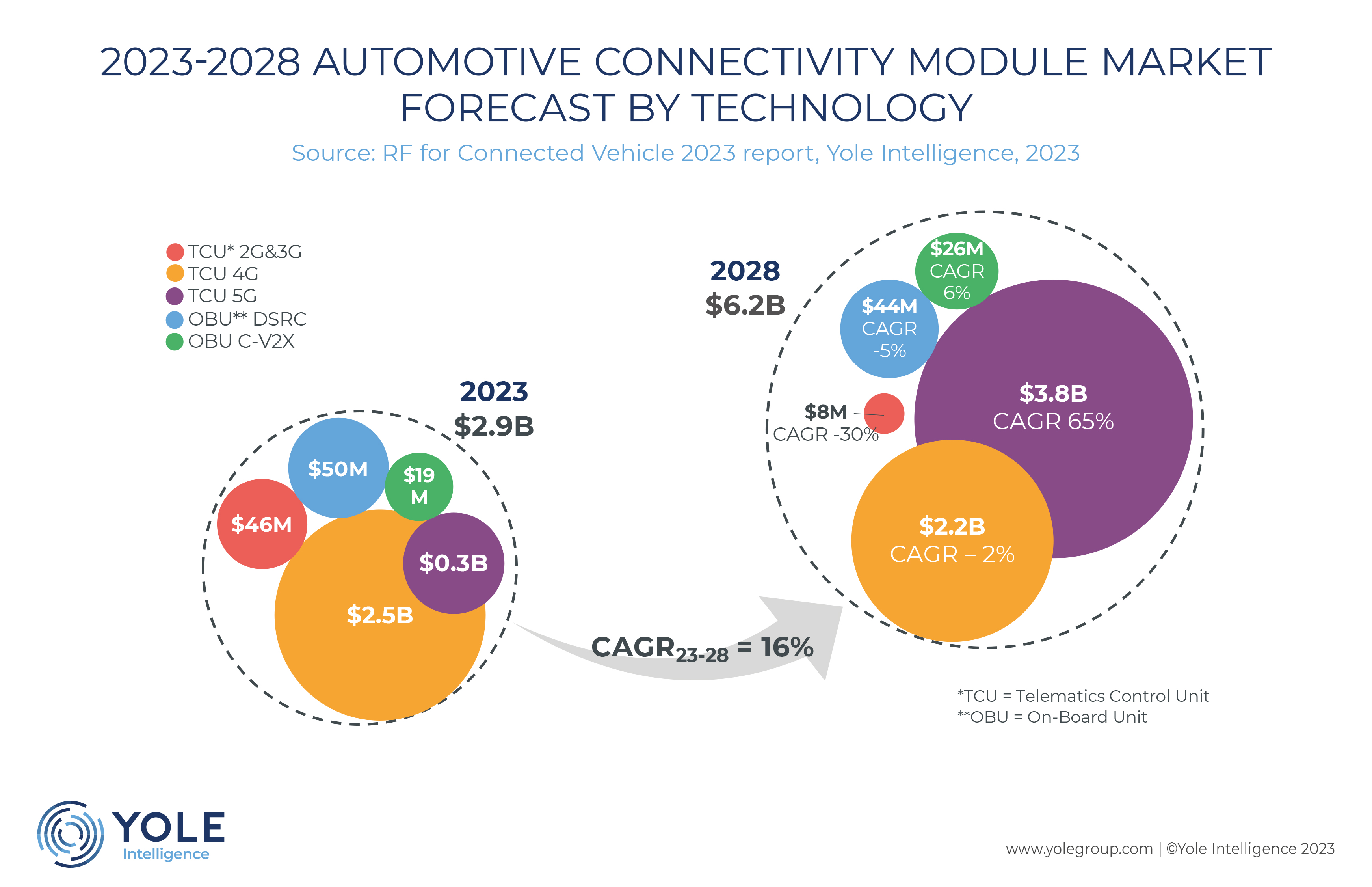
The connectivity module market is projected to grow from $2.9 billion in 2023 to $6.1 billion in 2028 with a CAGR23-28 of 16%.
Nevertheless, according to Yole Intelligence, the landscape is evolving rapidly, with compelling use cases like Teleoperated Autonomous Vehicles and Automated Valet Parking expected to be implemented by the end of the decade. NCAP programs, especially China NCAP and EuroNCAP, are also driving V2X adoption as soon as 2025.
“Telematics adoption is driven by lucrative business opportunities, offering enhanced user experience and valuable data for OEMs. Mandatory connectivity-based safety features like eCall and ISA are expanding globally. The adoption of 5G connectivity is influenced by higher costs and the absence of a definitive killer application, but it aligns with software-defined architecture for advanced autonomous driving,” said Raphaël Da Silva, Technology and Market Analyst within the Power and Wireless Division at Yole Intelligence.
Yole Intelligence, part of Yole Group, has combined its long expertise in semiconductors and its deep knowledge of automotive connectivity technologies and markets to deliver this first edition of the RF for connected vehicles report. This study provides valuable market metrics and forecasts for automotive connectivity. It analyses the drivers and challenges for automotive connectivity adoption and presents the main technological trends and ongoing developments in automotive connectivity with a focus on 5G RedCap and GNSS correction services. This report also discusses the main players across the automotive connectivity supply chain and analyses how the business models and supply chains are evolving.
“The automotive connectivity landscape has evolved with the introduction of technologies like 5G and C-V2X. In the 4G era, Intel, HiSilicon, and Qualcomm served the market, but Qualcomm took the lead in 5G after HiSilicon and Intel exited the business. Samsung and MediaTek entered the market recently, but qualification cycles in the automotive connectivity industry are long, so Qualcomm’s dominance is expected to continue in the short term,” said Cédric Malaquin, Team Lead Analyst for RF activity, at Yole Intelligence.
Regarding V2X, NXP initially led with its DSRC chipset, but due to regulatory challenges and the introduction of C-V2X, Autotalks and Qualcomm gained prominence. Qualcomm’s advantage lies in its scale and the integration of V2X in the cellular baseband, aligning with non-safety applications. However, for safety-related V2X applications in the future, Autotalks is expected to excel as a standalone V2X is necessary for ASIL-B certification.
In terms of GNSS, Qualcomm’s integration of GNSS capabilities in its cellular baseband impacted U-Blox’s position in the TCU business. However, with safety becoming a requirement for future applications, GNSS players like U-Blox are seeing renewed interest.
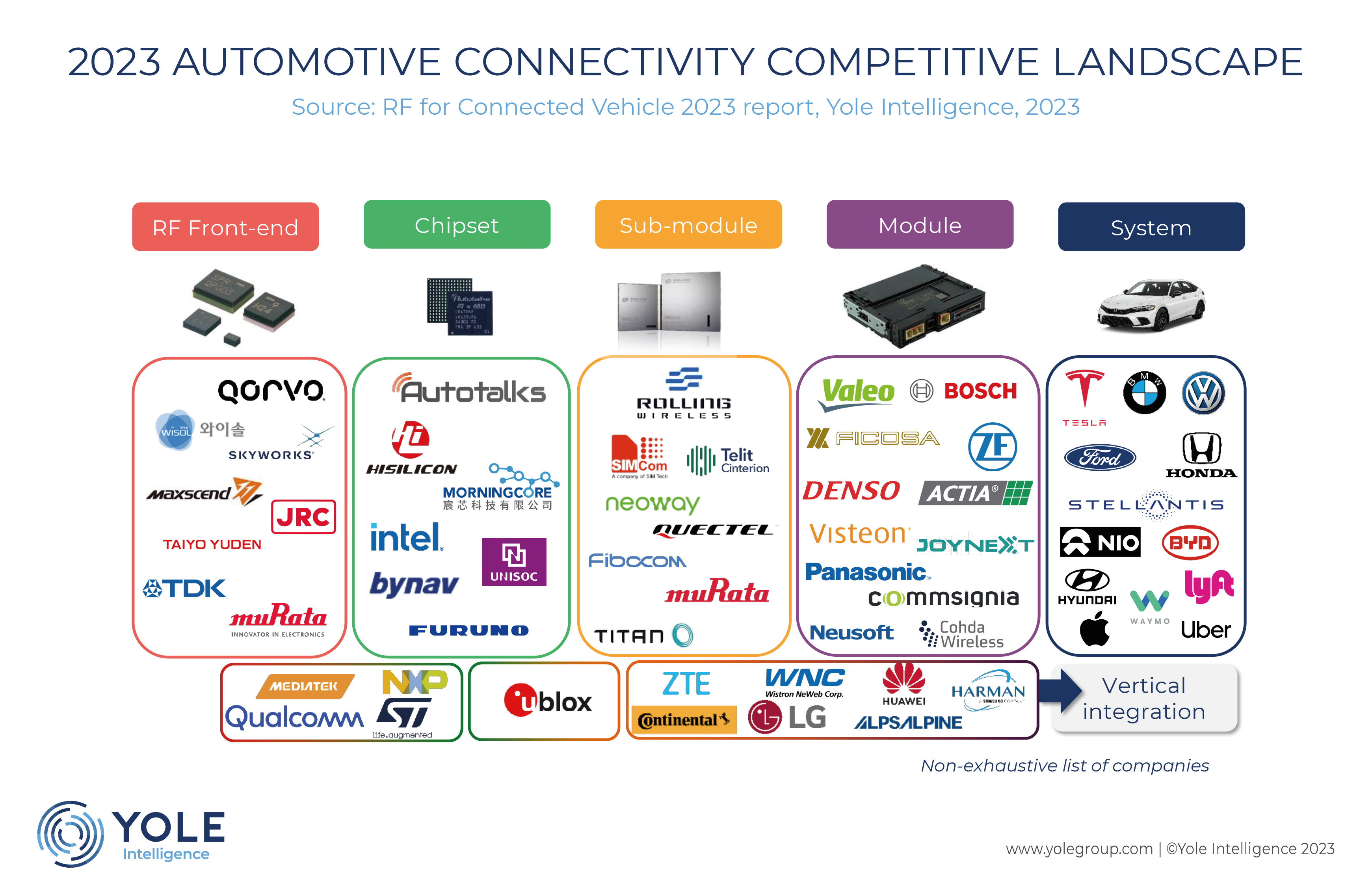
Consolidation has occurred among sub-system companies, such as the merger of Telit and Thales’ module business and the equity acquisition of Rolling Wireless by Fibocom. At the Tier 1 level, consolidation has already occurred, with Valeo acquiring Peiker and Samsung purchasing Harman. However, there are still numerous small-scale companies in the supply chain that may be acquired as the market continues to grow.





