Innovation within sustainable electronics manufacturing
In the aftermath of COP27, sustainability is once again at the forefront of global discussion. Debates surrounding emissions reductions, water security, and renewable energy are at centre-stage with many politicians, businesses, investors, and think tanks enthusiastic to bring about meaningful change.
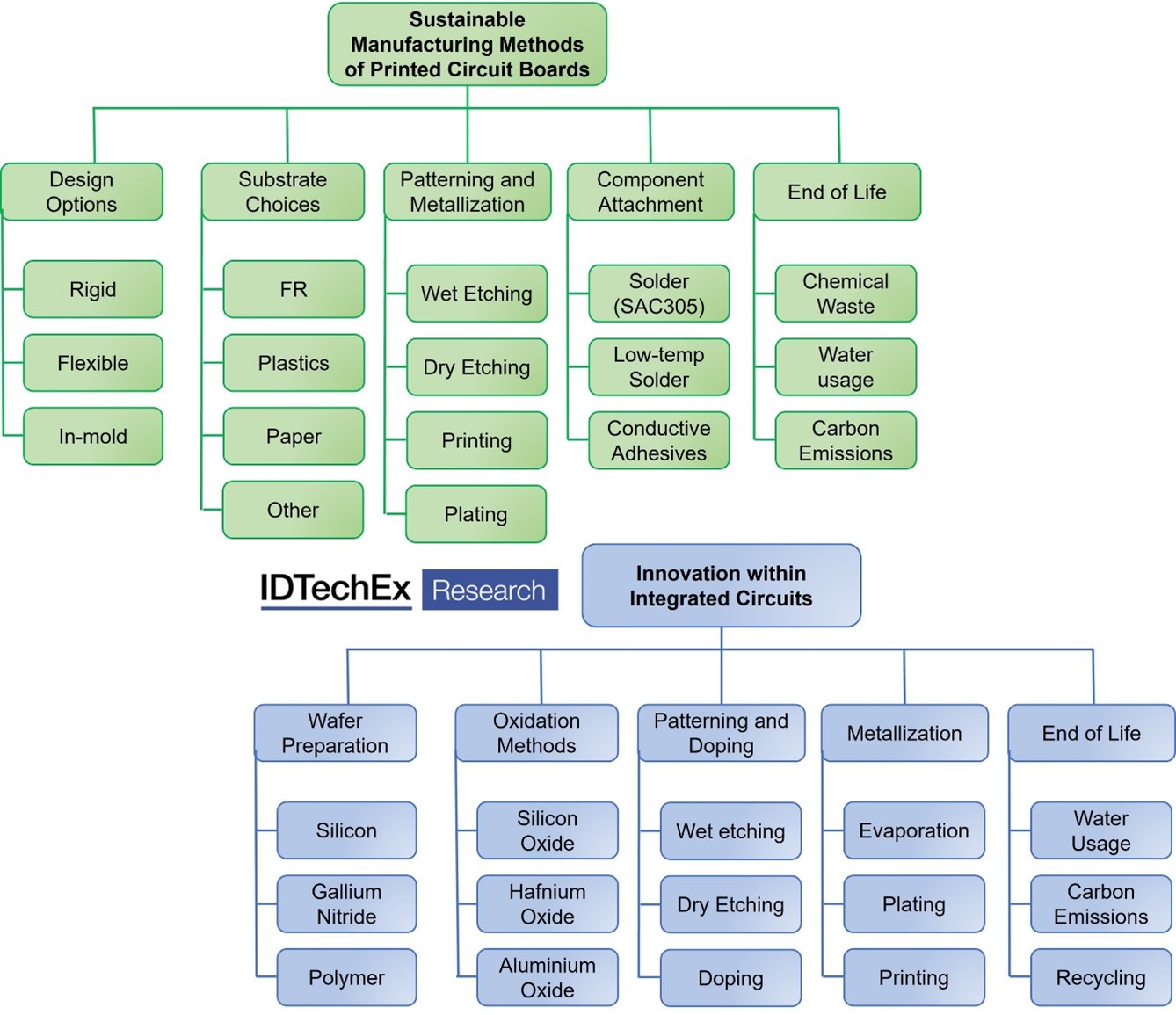
In IDTechEx’s report, Sustainable Electronics Manufacturing 2023-2033, methods of reducing emissions within one of the most polluting industries are evaluated and discussed with a view to cost-effective and widespread implementation.
With the electronics industry accounting for 4% of global greenhouse gas emissions, it is a sector that requires substantial innovation to reduce its environmental footprint. IDTechEx’s latest report explores how the environmental impact of manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and integrated circuits (ICs) can be reduced through innovative materials choices and processing methods. This includes implementing low-temperature processing, eliminating superfluous wasteful steps, recycling and re-using materials where possible, and adopting novel approaches where the long-term potential is foreseen. IDTechEx expects that within a decade, 20% of PCBs could be manufactured using more sustainable methods such as dry etching, printing, and low-temperature solder component attachment. The report explores what many well-known electronics manufacturers are doing to enact cost-effective and sustainable measures, including Samsung, IBM, Intel, Toshiba, Apple, and Dell, among others.
Sustainable manufacturing methods covered in this report
The report assesses sustainable methods of electronics manufacturing and concentrates on innovations within printed circuit boards and integrated circuits. The report evaluates how sustainable innovation can drive forward the new era of flexible electronics and covers different materials and manufacturing processes that can deliver effective long-term sustainability improvements. Covering each key stage of the value chain for PCB and IC manufacturing, the report identifies areas that can benefit from innovation. These are compared not just in terms of the emissions, materials, and water consumption but also in terms of what is scalable and cost-effective to implement.
The analysis covers the following areas:
- Different material choices for PCB and IC substrates
- Alternatives to traditional wet etching.
- Additive approaches such as printing metallic traces.
- Low-temperature component attachment materials
- Shifts towards new dielectrics as integrated circuits reduce in dimension.
- End of life analysis
Emerging flexible electronics benefit from sustainable innovations
Most electronics today are manufactured on rigid substrates; however, flexible electronics are on the rise as a wide range of different application areas grow, including wearable technology and flexible displays. The flexible PCB substrate market is expected to reach US$1.2 billion by 2033, largely led by polyimide – a bendable plastic substrate already used in the PCB industry. Polyimide is an expensive material and is also environmentally unfriendly. The report discusses the use of cheaper materials such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) but also biodegradable materials such as paper and natural fibres. While these appear some way away from appearing in everyday devices, many household names have pursued pilot projects employing biodegradable PCBs, including Microsoft and Dell.
A key advantage to the next generation of electronics is that its success depends upon innovation. Liberated from traditional processing routes, pioneering approaches can be adopted from the get-go that save time, reduce waste, and cut emissions. These approaches may involve something relatively simple such as switching to low-temperature solder, or something more revolutionary such as adopting a partial or fully additive manufacturing approach. The advantages and compromises to implementing sustainable innovations are fully evaluated in IDTechEx’s report.
Key questions answered in this report
- What are the key policies and legislations to watch out for?
- What are existing low-emission technologies that can be implemented?
- What disruptive technologies are on the horizon?
- Which novel manufacturing routes are both sustainable, reliable, and scalable?
- How can additive manufacturing reduce costs and minimise waste?
- Where are the key materials growth opportunities?
- What are key players doing to improve sustainability?
To find out more about the new IDTechEx report Sustainable Electronics Manufacturing 2023-2033, including downloadable sample pages, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/SustainableElectronics.