100Gbps with 6G sub-terahertz device achieved
NTT DOCOMO, NTT Corporation, NEC Corporation, and Fujitsu jointly announced the development of a top-level (1) wireless device capable of ultra-high-speed 100Gbps transmissions in the 100GHz and 300GHz sub-terahertz bands.
The four companies have been jointly conducting R&D on sub-terahertz devices since 2021 in anticipation of the coming 6G era. To date, tests of a jointly developed wireless device have achieved ultra-high-speed 100Gbps transmissions in the 100GHz and 300GHz bands at distances of up to 100 meters.(2) By comparison, 100Gbps is approximately 20 times faster than the maximum 4.9Gbps (3) data rate of current 5G networks.
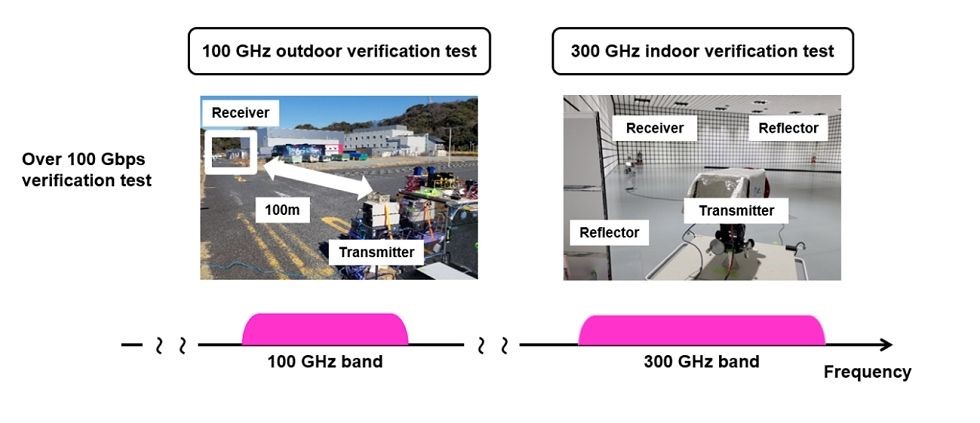
Verification test in the 100GHz and 300GHz bands
The roles and achievements of the four participating companies are described below.
DOCOMO
After analysing the wireless system configuration and performance required for 100GHz telecommunications applications, DOCOMO developed wireless transmission equipment capable of transmitting data rates equivalent to 100Gbps at a distance of 100 meters.
NTT
Based on research into 300GHz wireless devices and related equipment such as wideband mixers, NTT developed a top-level wireless device capable of transmitting 100Gbps per channel at a distance of 100 meters in the 300GHz band.(1)
NEC
After analysing a wireless system configuration for telecommunications in the 100GHz band, NEC developed a multi-element active phased array antenna (APAA) (1) consisting of more than 100 antenna elements.
Fujitsu
After researching compound semiconductor technologies that enable high-output, high-efficiency signal amplification to extend communication range and reduce power consumption in the 100GHz and 300GHz bands, Fujitsu achieved the world's highest power efficiency (4) in a high-output amplifier.
In the 6G era, when wireless networks are envisioned supporting diverse applications ranging from ultra-HD video streaming to real-time control in autonomous vehicles, as well as increasing communication demands, high-capacity wireless communication is expected to be achieved by exploiting the abundant bandwidth available in the sub-terahertz band from 100GHz to 300GHz. However, compared to 28GHz and other millimetre bands used in current 5G systems, the much higher frequencies of the sub-terahertz band will require entirely different wireless devices that are now being developed from scratch. To be successful, this effort will need to overcome several key challenges, such as determining the specific performance requirements of wireless devices operating in the sub-terahertz band, and then actually developing such devices.
Going forward, the four companies will continue to conduct extensive R&D into sub-terahertz telecommunications, leveraging each company's strengths in various initiatives to contribute to 6G standardisation.
Note: The research and development mentioned herein includes results from the ‘Research and Development for Expansion of Radio Wave Resources’ project conducted on behalf of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications.
[1] This assumes that as of March 2024, no other entity has announced 1) achievement of 100 Gbps transmission over a distance of 100 meters in the 100GHz band (according to NEC); 2) achievement of 100Gbps transmission over a distance of 100 meters in the 300GHz band (according to NTT); and 3) achievement of an equivalent isotropic radiation power (EIRP) of 50dBm and a beam steering angle of approximately ±30 degrees using 100 or more APAA elements in the 100GHz band (according to NEC).
[2] The transmitter and receiver are facing each other in a straight line with no obstacle between them.
[3] Maximum values specified in technical standards, but not representing the actual data rate, provided on a best-effort basis. Actual data rates may vary depending on the communication environment and network congestion.
[4] World's highest efficiency under specific high-power conditions in the 100GHz and 300GHz bands, respectively, according to Fujitsu as of March 2024.










